compendium |
|
transfer function
|
|
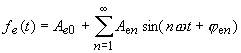 |
(47) |
| leads to the effect (output parameter) | |
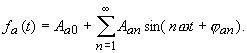 |
(48) |
| The calculation of the input spectrum Aen, φen to the output spectrum Aan, φ an is done using the so called transfer function of the circuit (the system) Normally it is the ratio of the phasor of an output parameter to the phasor of the input parameter causing it: | |
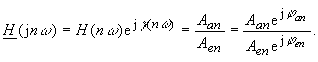 |
(49) |
| The transfer function H(φnω
) is derived from the circuit using the practices known from
calculating alternating currents . When deriving the transfer function it is important to remember using : |
|
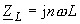 |
|
| or respectively | |
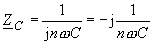 |
|
| for the complex resistance of the dummies |